Multimodal regenerative protocol for oral submucous fibrosis combining autologous fat grafting with piezo coronoidotomies and fascia release
Edward KO1,2,5,7, Chi-Huang Tseng2,3, Rebekah C Yang2,8, Yong-deok Kim4, Kazuto Hoshi5, Tetsu Takahashi6, Tsai-Ming Lin7, Chien-Chih Chen9.
1Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan; 2Liberty Lab of Tissue Engineering Takao, Kaohsiung, Taiwan; 3Division of Oral Pathology and Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan; 4Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea; 5The Department of Oral-Maxillofacial Surgery and Orthodontics, The University of Tokyo Hospital, Tokyo, Japan; 6Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Southern Tohoku Fukushima Hospital, Koriyama, Fukushima, Japan; 7Charming Institute of Aesthetic and Regenerative Surgery (CIARS), Kaohsiung, Taiwan; 8Fei Rou Physical Therapy Clinic, Kaohsiung, Taiwan; 9Traditional Medicine, Kaohsiung Veteran General Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
Background: Oral submucous fibrosis (OSF) is a chronic fibrotic disorder commonly induced by areca nut-slake lime exposure. It causes progressive mucosal rigidity and trismus. While conventional approaches—such as corticosteroids, split-thickness skin grafts (STSG), and mucosal excisions—can temporarily improve mouth opening, they often fail to reverse the fibrotic environment. We present a multimodal protocol integrating surgical release with autologous fat grafting, which has regenerative potential due to the presence of adipose-derived stromal cells (ADSCs) and anti-fibrotic signaling.
Methods: We retrospectively evaluated 10 OSF patients (6 male, 4 female; age 42–58) treated with the following protocol: (1) Piezo-assisted bilateral coronoidotomies, (2) micro-fat injection via MAFT gun (1/90 ml aliquots), (3) fascia adhesion release—initially performed using a 19-gauge needle and recently replaced by long mosquito forceps for more effective blunt dissection, (4) postoperative mouth-opening exercise, and (5) acupuncture at standard facial and limb points. Autologous fat was harvested from the abdominal region, centrifuged, and injected into the buccal/labial mucosa. Pre- and post-treatment biopsies were stained with H&E and Masson’s trichrome. Comparative data were also obtained from patients treated using STSG for OSF.
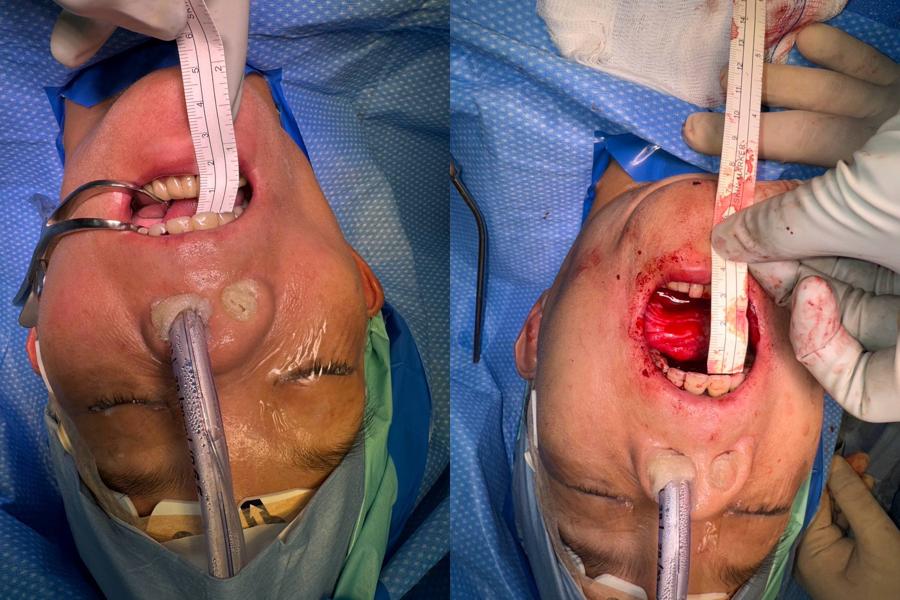
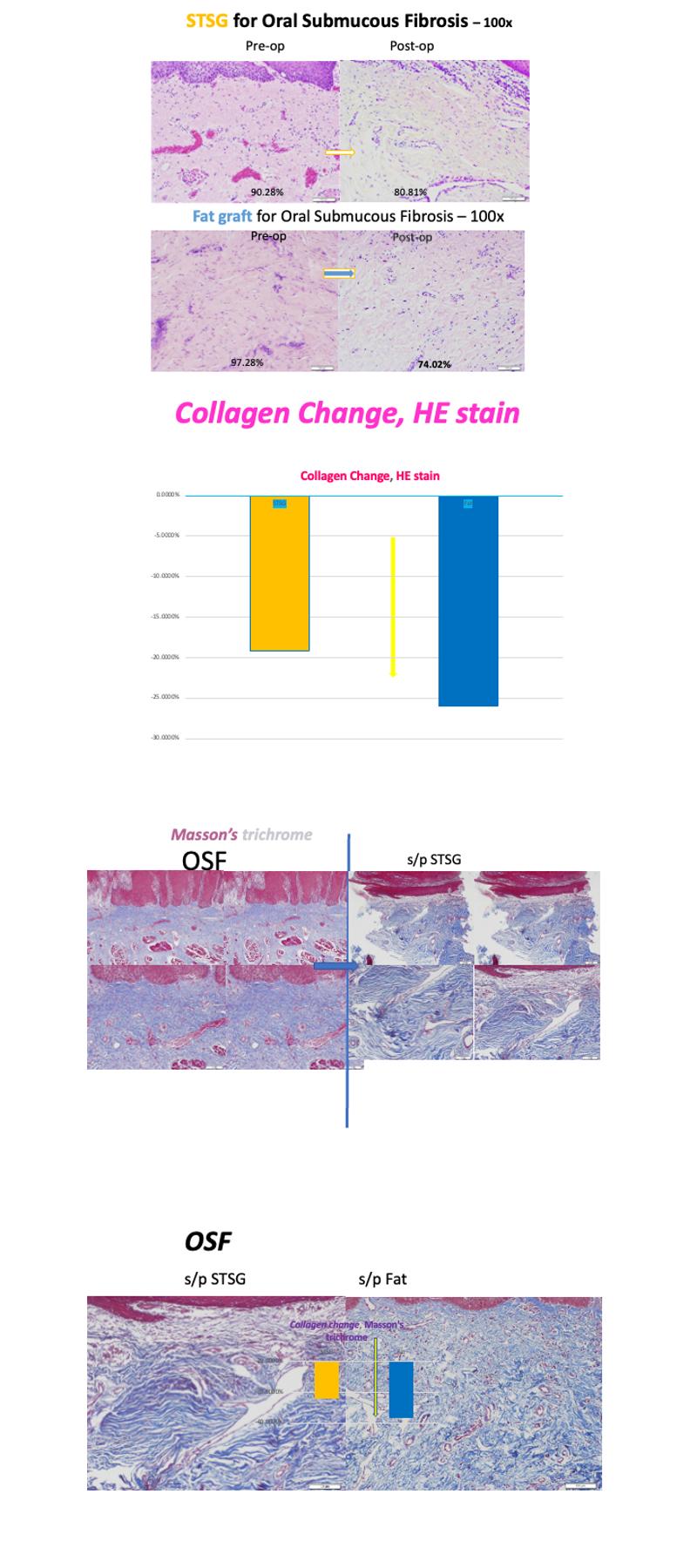
Results: The average increase in interincisal distance was 18.7 mm (range: 12–26 mm). Histological analysis revealed significant extracellular collagen reduction following fat grafting (from 97.28% to 74.02%) compared to STSG-treated sites (80.81% collagen post-op). Masson staining corroborated the improved tissue pattern with reduced fibrosis and enhanced elasticity. Postoperative mucosa was more pliable and moist, promoting improved patient compliance with physiotherapy. Pain reduced significantly (VAS score: avg. 7 to 2 within 72 hours), and no graft rejection or infection occurred.
Conclusion: This multimodal protocol offers a reproducible and biologically driven strategy for treating OSF. Autologous fat grafting not only restores volume but also promotes histologic remodeling through ADSC-mediated pathways. The replacement of the 19-gauge needle with long mosquito forceps for fascia adhesion release has further improved surgical efficacy by enabling safer and more comprehensive dissection. This method yields durable improvements in mouth opening and mucosal pliability, offering a promising regenerative alternative to traditional STSG-based reconstruction. Molecular-level investigations (e.g., VEGF, CD31, elastin) are ongoing.
[1] Oral submucous fibrosis, Autologous fat grafting, Tissue regeneration, Coronoidotomy, Engraftment promotion