CD38 promotes regulatory T cells survival by activating the calcium/Ras/GGT1 pathway to reduce ROS and induce post-transplant immune tolerance
Jian Gu1, Qufei Qian1, Ling Lv2.
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, People's Republic of China; 2The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, XuZhou, People's Republic of China
Liver transplantation requires lifelong immunosuppressive drugs to maintain intrahepatic immune balance and prevent transplant-related immune mediated adverse events. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) play an essential role in inducing immune tolerance. 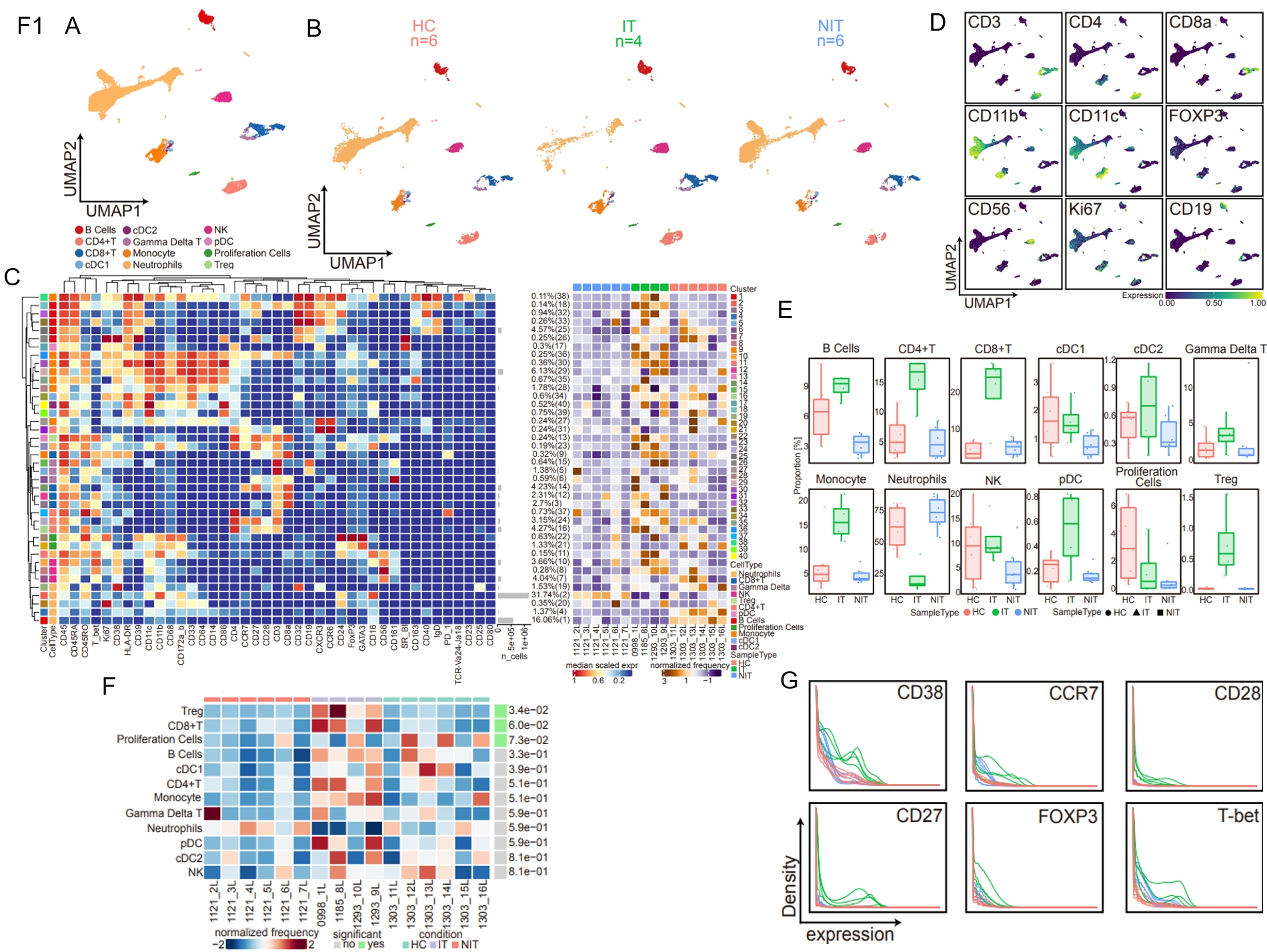 This study aimed to investigate mechanisms underlying transplant immune tolerance. Using mass cytometry, we found a higher proportion of CD38hi Tregs in the peripheral blood of patients who discontinued immunosuppressive drugs after liver transplantation.
This study aimed to investigate mechanisms underlying transplant immune tolerance. Using mass cytometry, we found a higher proportion of CD38hi Tregs in the peripheral blood of patients who discontinued immunosuppressive drugs after liver transplantation. 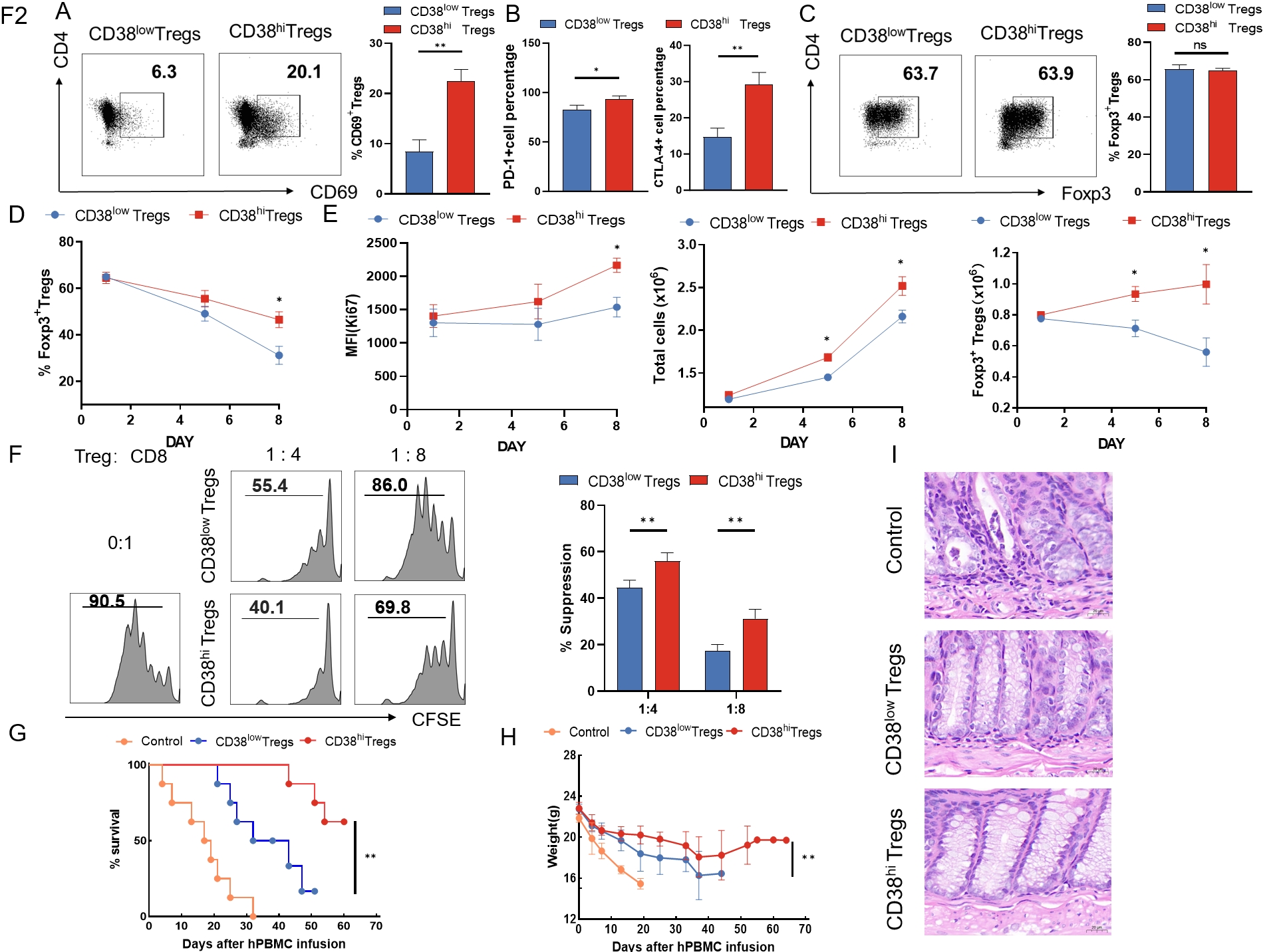 CD38 elevated the suppressive ability and survival of Tregs by improving oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) while reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS). Total proteomic analysis, untargeted metabolomics, and biochemical experiments revealed that CD38 activated calcium signaling which in turn initiated Ras/NF-κB signaling. Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT1), which is transcribed by NF-κB was upregulated in CD38hi Tregs. GGT1 plays a vital role in sustaining Treg survival and overcoming ROS injury by degrading exogenous GSH and increasing intracellular glutamate, cysteine, and glycine, thereby indirectly promoting endogenous GSH synthesis. In both humanized xenogeneic-graft-versus-host disease and skin transplantation models, injection of CD38hi Tregs alleviated inflammatory infiltration in target organs and prolonged survival. This study deepened our understanding of immune tolerance following transplantation and CD38hi Tregs represent a new target for monitoring and promoting immune tolerance after liver transplantation.
CD38 elevated the suppressive ability and survival of Tregs by improving oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) while reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS). Total proteomic analysis, untargeted metabolomics, and biochemical experiments revealed that CD38 activated calcium signaling which in turn initiated Ras/NF-κB signaling. Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT1), which is transcribed by NF-κB was upregulated in CD38hi Tregs. GGT1 plays a vital role in sustaining Treg survival and overcoming ROS injury by degrading exogenous GSH and increasing intracellular glutamate, cysteine, and glycine, thereby indirectly promoting endogenous GSH synthesis. In both humanized xenogeneic-graft-versus-host disease and skin transplantation models, injection of CD38hi Tregs alleviated inflammatory infiltration in target organs and prolonged survival. This study deepened our understanding of immune tolerance following transplantation and CD38hi Tregs represent a new target for monitoring and promoting immune tolerance after liver transplantation.
National Natural Science Foundation of China (81971495, 82171759, 82101873). CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (2019-I2M-5-035).
[1] Tregs
[2] CD38
[3] liver transplantation
[4] cell survival