
Reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation by engineered exosomes coated prussian blue nanozyme for specific targeting and acute liver injuries treatment
Qiuxia Zheng1, Jia Yao2, Zongbin Sun1, Yue Zhang1, Xun Li1,2.
1First Clinical Medical College, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, People's Republic of China; 2First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, People's Republic of China
Lanzhou University. Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Regenerative Medicine.
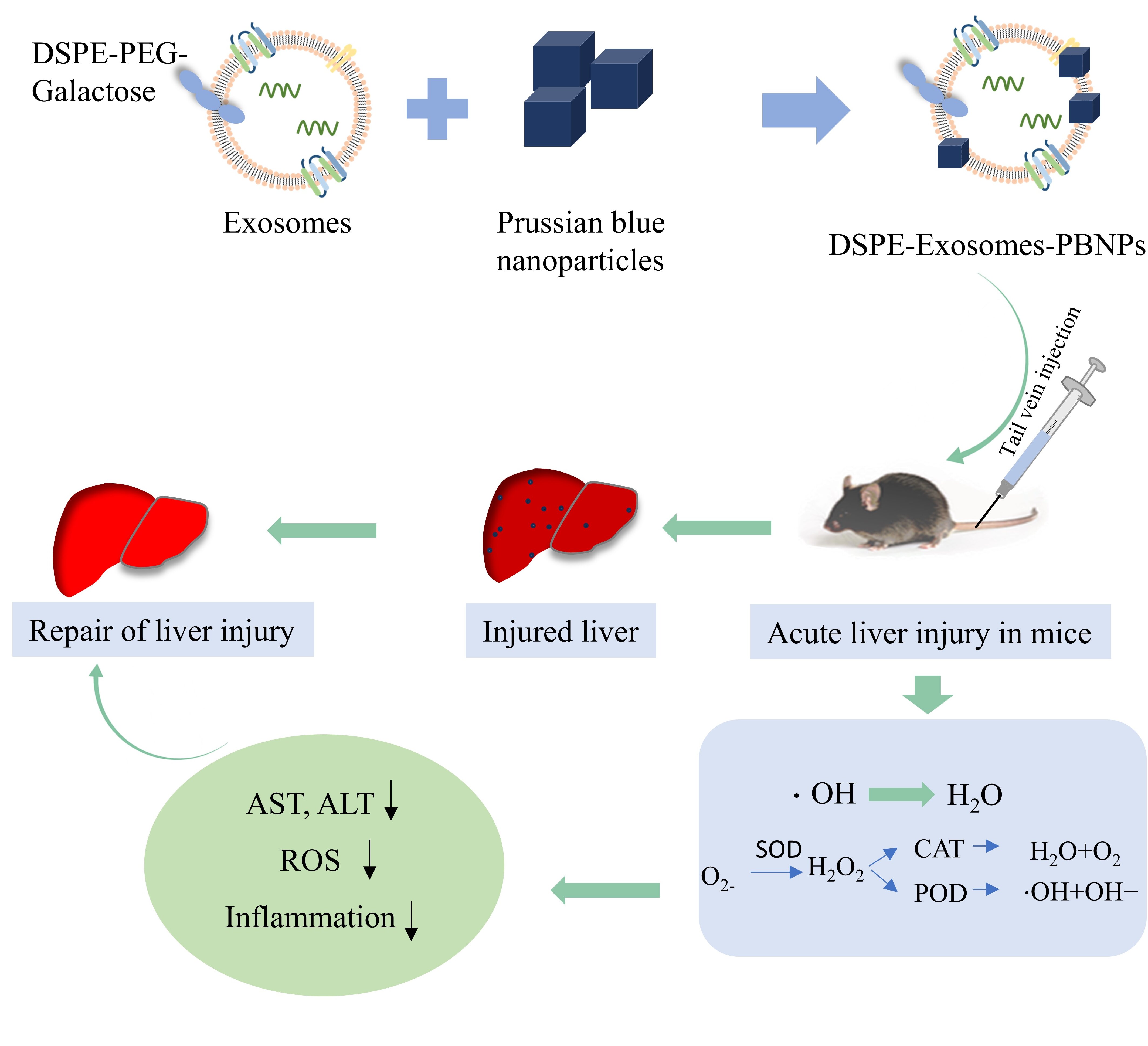
Introduction: Acute liver injury (ALI) is a potentially fatal condition characterized by the acute necrosis and apoptosis of hepatocytes, as well as the production of large quantities of free radicals and inflammatory factors. There is no effective programmatic intervention for the treatment of ALI other than liver transplantation. Prussian blue nanoparticles (PBNPs) have recently been shown to be a promising anti-inflammatory antioxidant with liver protection effects. However, its targeting to hepatocytes and bioavailability need to be improved.
Methods:In this study, the amphiphilic small molecule copolymer 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[poly(ethylene glycol)]-galactose (DSPE-PEG-galactose),which targets the hepatocyte surface receptor ASGPG, to modify exosomes secreted by umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Subsequently, the exosomes modified with DSPE-PEG-galactose were combined with Prussian blue nanoparticles (PBNPs) by extrusion to obtain a multifunctional nanosystem (DSPE-Exosomes-PBNPs). Within this multifunctional nanoparticle mixture, the DSPE-Exosomes reduce the immunogenicity of the nanoparticles and effectively enhance their ability to home to a damaged liver, achieving active targeting of hepatocytes. Additionally, the combined action of the exosomes and PBNPs exerts anti-ROS and anti-inflammatory effects, thereby initiating liver tissue repair. Using these components together can enhance the overall effect synergistically, accelerating the recovery of acute liver injury.
Results:The prepared DSPE-Exosomes-PBNPs exhibited excellent compatibility with cells and tissues, and their effective liver targeting enhanced hepatocyte uptake and liver tissue accumulation. Small animal imaging experiments revealed significant enrichment in liver tissue in cases of acetaminophen (APAP)-induced acute liver injury (ALI).Furthermore, DSPE-Exosomes-PBNPs reduced the expression of inflammatory factors and serum liver transaminase levels in the livers of mice with acute liver injury and played an anti-apoptotic role.
Conclusion:DSPE-Exosomes-PBNPs can be considered a promising hepatoprotective nanodrug delivery system for alleviating APAP-induced acute liver injury with excellent bioavailability and efficient hepatoprotective effect, which may provide an effective strategy for the prevention and treatment of APAP-induced acute liver injury.
This work was supported by Grant(s) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32160230), Special Projects for Scientific and Technological Achievements and Applications of Gansu Province (24ZDCA008), Talent Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project in Chengguan District, Lanzhou City, Gansu Province (2022RCCX0024)..
[1] Specific targeting
[2] Acute liver injury
[3] Anti-inflammatory
[4] Prussian blue nanoparticles
[5] Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes
[6] Sustained release
[7] Specific targeting